The geographical dispersion study has as objective to analyze
the several possible topological scenarios and verify how the variation of the number of nodes
affects the percentage of sites within different distance ranges (clustering effect).
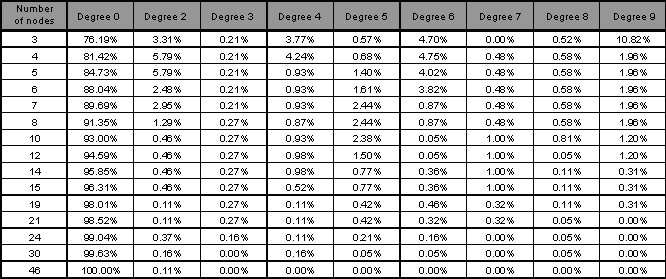
This study shows the percentage of sites associated to each node within the several distance
ranges in each topology and shows clearly when the variation of the number of nodes stops to be
effective regards placing more sites within the smaller distance ranges.
The geographical dispersion study by itself isn't enough to identify the best WAN structure,
given the fact that such identification depends directly to the interconnection costs
(Many of them not distance sensitive). However, such study gives us a very good view about
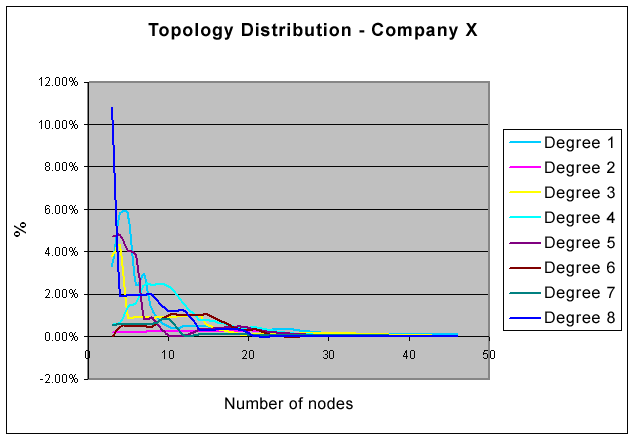
which topology probably will be the more adequate. In the graphic shown bellow we try to
demonstrate the specific clustering effect of a given organization. This effect is demonstrated
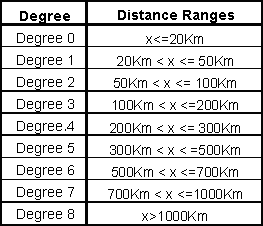
through the variation of the percentage of sites located within eight distance ranges, as follows: